Speed of Light
Introduction
Lunar Orbital Motion
Quranic Method for The Determination Of The Greatest Speed C
Defining the Variable Speed of Light
External Links
Speed of Light
The greatest speed C, denoting the velocity of light in vacuum, is hinted at in two glorious Quranic verses relating this fundamental universal constant C with the motion of the Earth-Moon system. A new relativistic interpretation of this Quranic relation gives C=299792.5 km/s in an extremely marvelous agreement with the accepted international value. This astonishing result emphasizes the unity of the physical world, the validity of the special theory of relativity and the authenticity of the Glorious Quran for unbelievers.
Introduction
The velocity of light C in vacuum belongs to a small group of the fundamental constants; however, it occupies an outstanding position even within this group. It is so important that it is encountered in very different branches of physics.
From the ancient Greeks down to the Middle ages, the speed of light was believed to be infinite. Aristotle believed that light propagates instantly. In the eleventh century, an Arabic scientist Alhassan suggests that light travels at a finite speed. Galileo (1600) tried this speed but he failed saying that light is extraordinarily rapid(l). Roemer (1676) was the first to measure the value of C using the eclipses of the Jovian satellite. He obtained an inaccurate value of C (215000 km/s) because the diameter of the earth's orbit was not known exactly. Froome's value was considered to be the most accurate for a long period until 1983 when the modulated laser radiation interferometers were applied for the determination of C with great precision.
According to the US National Bureau of Standards: C = 299792.4574 + 0.0011 km/ and according to the British National Physical Laboratory C = 299792.4590 + 0.0008 km/s
A basically new definition of the metre was accepted in October 1983 at the 17th General Conference on Measures and Weights(3):
"The metre is the length of the path traveled by light in vacuum during a time interval of 1/299792458 of a second".
The fixation of the value of C after the formation of the new definition of the meter does not mean yet the end of the story of this fundamental constant C. There are numerous other questions dealing with the relation between this multifarious, enigmatic constant C and the theory of Relativity.
Recalling the second postulate of the special theory of relativity declared by Albert Einstein (1905):
"The velocity C of light in vacuum is the same in all inertial frames of reference in all directions and depend neither on the velocity of the source nor on the velocity of the observer".
Pauli(1958) said that the data on binary stars allowed us to consider this postulate of the constancy of the velocity of light to be almost certainly correct.
According to Einstein's general theory of relativity (1917), the law of the constancy of the velocity C of light in vacuum can not claim any unlimited validity because the curvature of rays of light can only take place when the velocity of propagation of light varies with position. Einstein himself solved this contradiction between special and general relativity declaring in his paper written (1917):
"The results of the special relativity hold only so long as we are able to disregard the influence of gravitational fields on the phenomena".
This validity condition of the second postulate of special relativity is considered in the present work because the constancy of the velocity C needs absolute space (vacuum). To attain vacuum in the Einstein's sense of this word. it is not: sufficient just to eliminate from a volume of space every atom, molecule and particle, it is necessary also to get rid of the gravitational field. Therefore we have to screen out the effect of the solar gravitational field on the geocentric orbital motion of the moon, according to the applied Quranic equation; as a standard measure reference for evaluating the greatest cosmic speed described in the Holy Quranic verses.
Lunar Orbital Motion
The ARAB people use the lunar system in their calculation of time. The Quran addressed them in the only language they could understand without upsetting their habits. GOD (in Arabic ALLAH: the ONE and Only GOD, the CREATOR) says in the Quran:
| “ | It is He Who made the sun to be a shining glory and the moon to be a light (of beauty), and measured out stages for her; that ye might know the number of years and the count (of time). Nowise did Allah create this but in truth and righteousness. (Thus) doth He explain His Signs in detail, for those who understand | „ |
| [Qur'an 10:5] | ||
The lunar year is twelve months, the month is defined recently as the time of one revolution of the moon in its orbit around the earth. God hints at such orbit in the Quran:
| “ | It is He Who created the Night and the Day, and the sun and the moon: all (the celestial bodies) swim along, each in its rounded course | „ |
| [Qur'an 21:33] | ||
Here an essential scientific fact is clearly stated, namely, the existence of the earth's, sun's and moon's orbits; besides, a reference is made to the traveling of these celestial bodies in space with their own motion. A new concept had therefore been established in the Quran, hundreds of years before it was discovered by modern science.
Today the concept of the lunar year is widely spread and, as we know, the moon is our nearest neighbor in space, and a companion to our planet. It is often said that the earth and moon form a twin-planet. As the moon orbits around the earth, the change in the relative positions of the moon, earth and sun cause the moon to show its phases(8-9). The time between consecutive new moons is 29.53 days and is called the synodic month. During this time, however, the earth, and consequently the moon's orbit, have traveled some way around the sun, so the position of the moon against the background of stars is different. 'l;he time for the moon to return to the same position in the sky as viewed from earth is called the sidereal month (27.32 days) which represents the actual real net time of one revolution in the moon's orbit. This orbit is almost circular having an average radius r=384264 km.
Referring to the Quranic verse [Qur'an 10:5], we notice that it discriminates between the apparent synodic period for knowing the number of years and the real sidereal period for reckoning in scientific calculations. These two systems of measuring time are now given in the text books of Astronomy.
| sidereal month | 27.321661547 + 0.000000001857×y days |
| synodic month | 29.530588853 + 0.000000002162×y days |
In these verses the sideral system should be used for both the lunar month and the terrestrial day as accurate measured periods (with respect to a distant apparently fixed star).
Quranic Method for The Determination Of The Greatest Speed CThe length of the moons' orbit L and the time t of one terrestrial day are correlated in a marvelous Quranic verse which describes a universal constant velocity of a certain cosmic affair as follows:
the Quranic expression "of your reckoning" leaves no doubt as to our understanding of the year as the lunar year. The verse begins with a reference to a certain "cosmic affair" which GOD creates and commands. This affair travels, permanently through the whole universe between the heavens and the Earth, so speedily that it crosses in ONE DAY a maximum distance in space equivalent to that which the moon passes during ONE THOUSAND LUNAR YEAR (i.e. during 12000 Sidereal months: When the Earth-moon system is still inside the solar system the position of the sun relative to Earth with respect to stars changes; this means that the moon has to make more than 360 degrees with respect to stars in order to point to the sun again. However when the Earth-moon system exits the solar system the position of the sun relative to Earth with respect to stars remains the same, that is, the moon now only has to make 360 degrees with respect to stars in order to point to the sun again (the synodic periods become equal to the sidereal periods). This means that the lunar month with respect to the sun becomes equal to lunar month with respect to stars and Earth day with respect to the sun becomes equal to Earth day with respect to stars. So the 1000 lunar years with respect to sun become equal to 12000 lunar months with respect to stars. Also when astronomers study the energy of orbits they use the sidereal system, that is, the moon has to return to the same position with respect to stars and not return to the same position with respect to the sun.) Distance crossed in vacuum by the universal cosmic affair in one sidereal day = length of 12000 revolutions of the moon around the earth.
where:
substituting R = 384264 km and T = the sidereal lunar month = 27.321661 days = 655.71986 hr
This value is given in all text books of astronomy and is accepted by NASA. The angle traveled by the earth moon system around the sun during one sidereal month of period 27.321661 days can be calculated if we take into consideration the period (365.25636 days)of one heliocentric revolution (1 year) of the earth-moon system.
Thus φ is a characteristic constant of this system depending on uniform periods of the month and the year. Since the presence of the sun changes the geometrical properties of space and time , we must screen out its gravitational effect on the earth moon system according to the validity condition of the second postulate of special relativity, i.e. we must only consider the lunar geocentric motion without the heliocentric motion of the earth-moon system. Thus a velocity component
From equation (1) and (3) we get a new Quranic relation for the earth moon system:
substituting the sidereal values of the periods t and T, the NASA value of the measured orbital lunar velocity V = 3682.07 km/hr., and the calculated value of cos@ = cos 26.92848 = 0.89157, we get the velocity of the cosmic affair from eq. 5 as expressed in the Holy Quran. C=12000 x 3682.07 x 0.89157 x 655.71986/86164.0906
It is very interesting to mention here the second Quranic verse that hints at the same relativistic Quranic equation in the earth-moon system: God Most High said:
| ||||||||||||||
Defining the Variable Speed of Light
In 1915 (10 years after special relativity) Einstein developed the theory called General Relativity that deals with gravitational fields and according to this theory the velocity of light appears to vary with the intensity of the gravitational field. For example, an observer outside gravitational fields measures the speed of light locally (in his location) at 299792.458 km/s but when he looks towards a black hole he sees the speed of light there to be as slow as a few meters/sec. At the same time an observer free falling into that black hole (zero-g) measures the speed of light locally (in his location) at 299792.458 km/s; when he looks towards the black hole he sees the speed of light there much slower; when he looks away from the black hole he sees the speed of light there much faster. If he tries to resist his free fall into that black hole (by firing his rockets for example) he will not measure the speed of light locally anymore at 299792.458 km/s; instead the stronger the g-force that he feels the faster light appears to him. Again when he looks towards the black hole he sees the speed of light there much slower; when he looks away from the black hole he sees the speed of light there much faster. In any case, free falling or not, he will never see the speed of light outside gravitational fields at 299792.458 km/s. Finally, there is no difference between the effects of g-forces experienced from these rockets and the effects of g-forces experienced when standing on planets, stars... hence an observer standing on a black hole measures the speed of light locally (in his location) much faster than 299792.458 km/s; when he looks towards outside gravitational fields he sees the speed of light there a zillion km/s.
12000 Lunar Orbits/ Earth Day = 299,792.458 km/s is the speed of light for observers standing outside gravitational fields and looking at light also traveling outside gravitational fields. But an observer near a black hole for example sees the speed of light outside gravitational fields a zillion km/s. In our case the event is the moon orbiting Earth. When an observer in stronger gravitational fields, near a black hole for example, looks at the Earth-moon system he does not see the moon orbiting Earth once every month; instead he sees the moon orbiting Earth once every few seconds; he also sees the length of the lunar orbit to be much longer than we see it. This is because the gravitational field that he is in causes his clock to run slower and his ruler to shrink.
Not only observers in different gravitational fields will not agree on the time period for the lunar orbit but also they will not agree on the length of the lunar orbit either. By using classical orbital mechanics we discovered that all observers will see the speed of light outside gravitational fields equal to 12000 Lunar Orbits/Earth Day; but from General Relativity we know that they will never agree on a value in km/sec. An observer near a black hole for example sees the speed of light outside gravitational fields a zillion km/s, but still equal to 12000 Lunar Orbits/Earth Day.
This means that if the speed of cosmic affairs outside gravitational fields were defined in km/sec then it would have appeared to vary for observers in different gravitational fields; however since this speed was defined in Lunar Orbits/Earth Day then it will never appear to vary to anyone because 12000 Lunar Orbits/Earth Day is common to all observers. Hence outside gravitational fields this equation in the Quran is true for all observers forever.
External Links
The Noble Qur'an
Order a free English translation of the Holy Qur'an.
Arabic Text of the Holy Qur'an.
Tafsir Ibn Kathir
Quran Recitation
BBC Report on this new method
www.speed-light.info


 is the velocity of the cosmic affair,
is the velocity of the cosmic affair,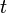 is the time interval of one terrestrial sidereal day defined as the time of one rotation of the earth about its axis (relative to the stars). i.e. 23 hr, 56 min, 4.0906 sec = 86164.0906sec.
is the time interval of one terrestrial sidereal day defined as the time of one rotation of the earth about its axis (relative to the stars). i.e. 23 hr, 56 min, 4.0906 sec = 86164.0906sec. is the inertial distance which the moon covers in revolution around the earth during one sidereal month i.e.
is the inertial distance which the moon covers in revolution around the earth during one sidereal month i.e.  is the measured average orbital velocity of the moon deduced from the average radius
is the measured average orbital velocity of the moon deduced from the average radius 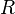 of the lunar geocentric orbit as measured from an orbiting earth during its heliocentric motion)
of the lunar geocentric orbit as measured from an orbiting earth during its heliocentric motion)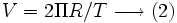
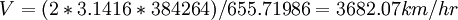


 representing the net orbital velocity of the moon is introduced for calculating the net length L of the lunar orbit assuming a stationary earth.
representing the net orbital velocity of the moon is introduced for calculating the net length L of the lunar orbit assuming a stationary earth.


